According to the new GST regime, an eWay bill is required to transport all taxable goods worth more than Rs.50,000 if the distance between the source and destination is more than 50km. Any transport
that doesn’t fall under this criterion does not require an eway bill. Further, the GST body has made certain goods and modes of transport exempted from eway bill generation to reduce the compliance burden on small and medium businesses (SMBs). This article discusses the key eway bill exemptions and the cases when eway bill is not required.
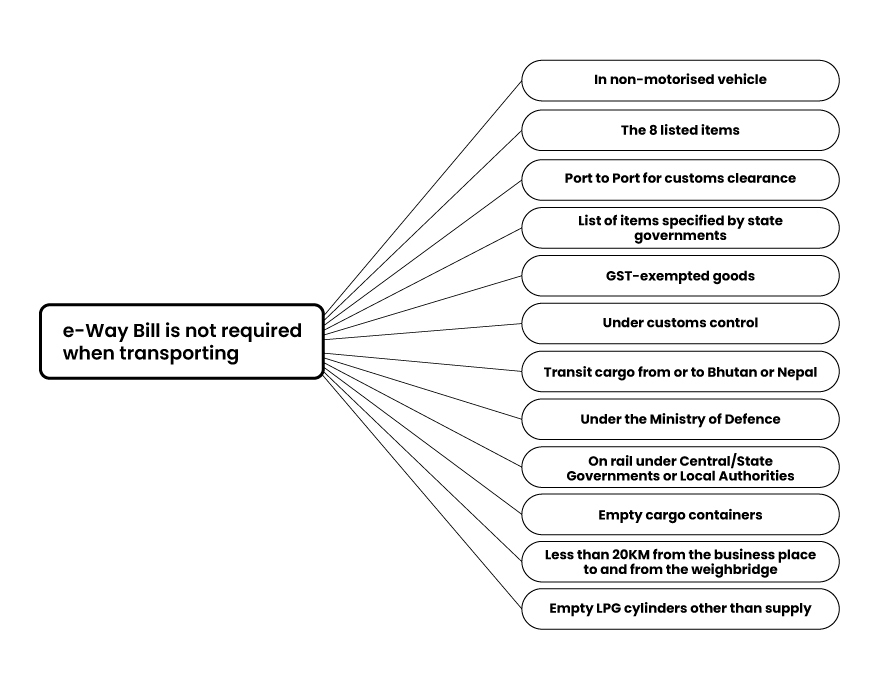
Cases When eWay Bill is Not Required
Less than 50km in Distance
If the distance between the source and destination station of the transport is less than 50km, an eway bill is not necessary irrespective of the state and city.
Goods Value Less Than Rs.50,000
If goods are worth less than Rs.50,000, e-way bill generation is not required. However, the transporter needs to carry relevant documents like invoices, bills, or delivery challans related to the consignment that clearly state the value of the goods being shipped.
Transport by Non-Motorized Vehicle
For goods moved via non-motorized vehicles (e.g., handcarts or bicycles), an e-way bill is not necessary. This exemption is particularly relevant in smaller towns and for micro-entrepreneurs who rely on low-cost transportation.
Goods Handled by Government Agencies
Goods transported by government entities like the Ministry of Defence or Central Government, State Government, or any local authority for non-commercial purposes don’t require an e-way bill. This covers goods under government schemes or initiatives.
Empty Containers or Unladen Vehicles
Empty containers or vehicles moving without a load don’t require an e-way bill, making logistics easier for transport providers.
Transportation by Rail or Air
If goods are being transported by rail, air, or waterway rather than by road, an e-way bill is generally not required.
Transit Cargo for Nepal or Bhutan
Goods transported through India for Nepal or Bhutan are also exempt, as they’re intended for international export rather than domestic trade.
Goods Transported for Customs Clearance
- Goods that are transported from the port, airport, air cargo complex and land customs station to an inland container depot or a container freight station for clearance by customs.
- Goods are transported under customs bond from an inland container depot or a container freight station to a customs port, airport, air cargo complex and land customs station or from one customs station or customs port to another customs station or customs port.
Exempted Goods
No e-way bill is required for transporting goods exempt from GST, like fresh fruits, vegetables, milk, or certain handicrafts. Here is list of the goods whose transport doesnt require eway bill.
- Live asses, mules and hinnies
- Live bovine animals
- Live swine
- Live sheep and goats
- Live poultry ducks, geese, turkeys and guinea fowls.
- Other live animal such as Mammals, Birds, Insects
- Meat of bovine animals, fresh and chilled.
- Meat of swine, fresh, chilled or frozen
- Meat of sheep or goats, fresh, chilled or frozen
- Meat of horses, asses, mules or hinnies, fresh, chilled or frozen
- Edible offal of bovine animals, swine, sheep, goats, horses, asses, mules or hinnies, fresh, chilled or frozen
- Meat and edible offal, of the poultry of heading fresh, chilled or frozen
- Other meat and edible meat offal, fresh, chilled or frozen
- Pig fat, free of lean meat, and poultry fat fresh, chilled or frozen
- Pig fat, free of lean meat, and poultry fat, salted, in brine, dried or smoked
- Meat and edible meat offal, salted, in brine, dried or smoked;
- Fish seeds, prawn/shrimp seeds whether or not processed, cured or in frozen state
- Live fish
- Fish, fresh or chilled
- Fish fillets and other fish meat
- Crustaceans, whether in shell or not, live, fresh or chilled;
- Molluscs, whether in shell or not, live, fresh, chilled
- Fresh milk and pasteurised milk, including separated milk, milk and cream
- Curd; Lassi; Butter milk
- Paneer
- Birds’ eggs, in shell, fresh, preserved or cooked
- Natural honey
- Human hair, unworked, whether or not washed or scoured; waste of human hair
- Bones and horn-cores
- Hoof meal; horn meal; hooves, claws, nails and beaks; antler, etc
- Semen including frozen semen
- Live trees and other plants; bulbs, roots and the like; cut flowers and ornamental foliage
- Potatoes & Tomatoes, fresh or chilled
- Onions, shallots, garlic, leeks and other alliaceous vegetables
- Cabbages, cauliflowers, kohlrabi, kale and similar edible brassicas, fresh or chilled
- Lettuce and chicory, fresh or chilled
- Carrots, turnips, salad beetroot, salsify, celeriac, radishes and similar edible roots, fresh or chilled.
- Cucumbers and gherkins, fresh or chilled
- Dried vegetables, Dried leguminous vegetables
- Root vegetables like Manioc, arrowroot, salep, Jerusalem artichokes, sweet potatoes
- Coconuts, Brazil nuts, and other nuts
- Bananas, Dates, figs, pineapples, avocados, guavas, mangoes and mangosteens.
- Citrus fruit, such as Oranges, Mandarins
- Melons, Papayas, and other fruits.
- Coffee beans, not roasted
- Green leaves of tea
- Seeds of anise, badian, fennel, coriander, cumin or caraway; juniper berries
- Fresh ginger, fresh turmeric
- Wheat and meslin, rye, barley, oats, Maize, Rice, Sorghum, Buck Wheat, cereal flours
- Soya beans, ground nuts, Linseed, sunflower seeds, and other oil seeds.
- Plants and parts of the plant, locust beans, cereal straw and husks, swedes, lac and shellac, betel leaves, lac and shellac, betel leaves.
- Jaggery of all types
- Puffed rice, papad, bread, water, non-alcoholic Toddy.
- Tender coconut water
- Aquatic feed
- Pulses, wheat bran and de-oiled caked
- Salt of all types
- Human Blood
- Contraceptives, all types
- Organic manure
- Kajal, Kumkum and related products
- Municipal waste, sewage sludge, clinical waste
- Plastic bangles
- Firewood or fuelwood
- Wood charcoal
- Stamp papers
- Postal items, like envelopes, postcards etc
- Cheques, lose or in book form
- Printed books, Newspapers, journals and periodicals
- Maps and hydrographic or similar charts
- Silkworm laying, cocoon
- Raw silk
- Silk waste
- Gandhi Topi
- Khadi yarn
- Coconut, coir fibre
- Indian National Flag
- Earthen pot and clay lamps
- Glass bangles
- Agricultural tools
- Handloom machinery
- Hearing aids
- Handmade musical instruments
- Slates, Slate pencils and chalk sticks
- Passenger baggage
- Puja samagri
- Liquefied petroleum gas for supply to household and non domestic exempted category (NDEC) customers
- Kerosene oil sold under PDS
- Natural or cultured pearls and precious or semi-precious stones
- Currency
FAQs on e-Way Bill Exemptions
When is an e-way bill not required?
An e-way bills aren’t required in cases where:
- Goods transported are valued at less than Rs.50,000.
- Non-motorized vehicles, like handcarts or cycles, are used.
- GST-exempted goods
- Empty cargo containers
- Goods are in transit for import/export to locations such as ports or international airports.
- Government bodies transporting goods for non-commercial purposes.
What documents are required if no eway bill is required?
Even when e-way bills are exempt, it’s advisable to:
- Retain purchase orders, invoices, and other relevant records.
- Keep updated with state-specific exemptions.
- Regularly review GST Council notifications for exemption changes.
What penalties apply if an e-way bill exemption isn’t applicable?
Transporting goods without an e-way bill when required can result in penalties, including confiscation of goods or fines. Ensuring compliance is essential to avoid such penalties.
Is eway bill required for hand delivery?
No, eway bill required only when the transportation happens in a motorised vehicle